MINIATURIZATION
What Is Hair Miniaturization?
Hair miniaturization is a process that is biologically driven by hormones. This phrase describes the process in which follicles shrink in size over an extended period of time and if untreated, will eventually leave the scalp bald.
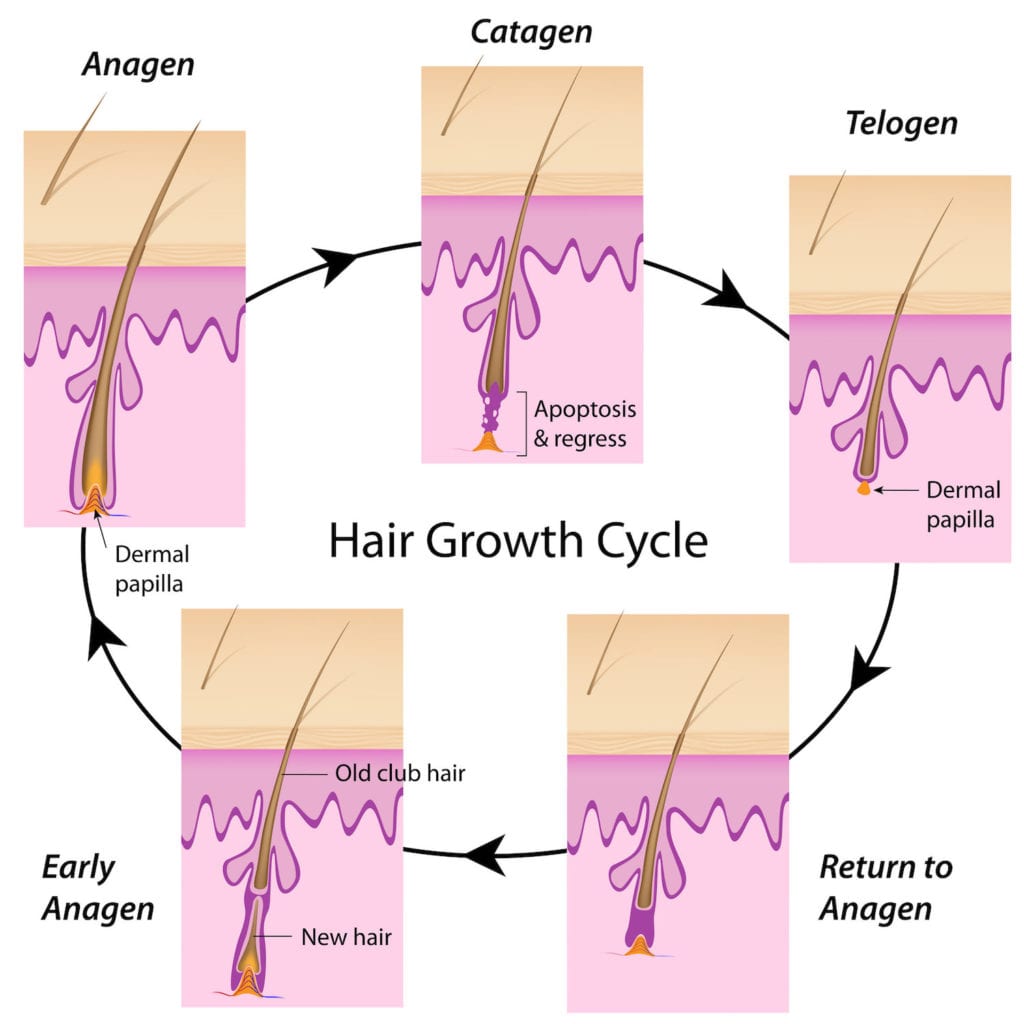
To better understand hair miniaturization, you need to understand the hair follicle growth cycle. This cycle consist of three main phases: #1 the growth phase (Anagen), the transitional phase (Catagen), and the resting phase (Telegen). In an ideal world, all of our hair follicles would remain in a growth phase, but we know that this is not always the case. In fact there are follicles on our head that are currently in every single one of those faces. The goal is to keep as many follicles in the growth phase as possible.
However, in genetically susceptible hair follicles, a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can cause the growth phase of the hair cycle to become dramatically shorter. The follicles that are susceptible to DHT are typically found (in men) on the top of the scalp. This is why most men can retain the hair on the side and back of their head for most of their lives. Unfortunately, the follicles on the top of your head that are susceptible to DHT are unable to grow to their full size because their growth phase is shorter and so they continue to decrease in size overtime until they eventually become nonexistent. This process is often referred to as male pattern baldness.
Recommended Intake
TheFDA recommended daily allowance of biotin is 30-100 mcg per day. High-dosage, in some cases 650 times the recommended daily intake, has been touted to help reverse hair loss. Normal levels of this vitamin are necessary to form keratin, the protein-making up skin, nails, and hair. However, high dosages have not been proven to improve hair loss. Male pattern hair loss and female pattern hair loss, in particular, are genetic and hormone-related and are not improved with high-dose biotin. Recent reports show that this can be dangerous.
Warnings About Taking High Dosages of Biotin
The FDA recently released an alert that high dose biotin can interfere with certain lab tests and cause incorrect test results. High levels of this in patients’ blood samples can cause falsely high or falsely low results, depending on the test. For example, this vitamin can make troponin levels appear low or normal when they may actually be elevated.
Elevated levels of troponin are a marker that the patient may be having a heart attack. If troponin levels appear low a heart attack could go undiagnosed. The FDA reported that a person on high-dosage supplementation died of a heart attack that went undiagnosed due to a falsely low appearing level of troponin.
High-dose biotin can also alter the results of thyroid tests such as TSH, T4, and T3. Hormone levels such as parathyroid hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), latinizing hormone (LH), and cortisol can also be affected. Vitamin D levels have also been found to be inaccurate. It is unlikely that recommended daily allowances of biotin will skew laboratory results. Before undergoing any of the above laboratory tests, anyone taking this supplementation should inform their healthcare provider.
Call MD Hair Labs to schedule your no-cost, no-risk consultation with our expert physicians and hair technicians about hair health!

